先进制造技术课程笔记
本文于 1182 天之前发表,文中内容可能已经过时。
临时抱佛脚的我又来了,罗列了先进制造技术这门课的问题。
一、能场部分
注1:EDM – Electrical Discharging Manufacturing
注2:EFM – Energy Field Manufacturing
1、创新与发明的区别在哪里?
答:创新(invention)是在已有事物的基础上进行某一方面的改动,比如,将电灯泡的灯丝材质由碳丝替换成钨丝。发明(innovation)相比于创新具有更强的创造性,一般是指从无到有的一个过程,比如合成一种全新的发动机材料、提出一套全新的运行方案。
2、能场的本质是什么?
答:是一种能量的分布形式,它能够向物体做功或者改变系统的状态。
The energy field is the spatial and temporal distribution of energy. The distributions of froces and energy are energy fields.
3、能场制造中的能场具有哪些形式?请列举出相应的例子,并说明能量与材料的具体作用原理。
答:力、电、光、辐射、热。增材制造:一种材料能从多个方向吸收能场的能量,吸收能量之后就会到达一个跟原来材料分离的状态而独立出来。
4、What are the two principal types of EDM processes? Describe the EDM process mechanism.
a) type 1, die-sinking EDM; type 2, wire EDM (WEDM);
b) EDM Process: Firstly, we move the tool immersed in dielectric liquid close to the workpiece. Then the dielectric liquid between the two electrodes breaks down and suddenly becomes conductive which contributes to high temperature. As a result, the surface of the workpiece will be removed.
5、Explain the different methods used to improve flushing in EDM.
a) controlling the fluid flow (normal flow, reverse flow, jet flushing, and immersion flushing);
b) modifying the electrode shape;
c) imparting relative movement between the workpiece and the tool electrode.
6、Why vibration can improve EDM process?
The high-frequency pumping action of the vibrating surface accelerates the slurry circulation and reduces the machining time. The vibrations can be imparted either to the workpiece or the tool electrode. These vibrations introduce acoustic streaming in the dielectric tank and particles move along this stream.
| 英 | 中 |
|---|---|
| ultrasonic | 超声波 |
| spatial | 空间性 |
| temporal | 瞬时性 |
| utilize | 应用 |
二、激光部分

1、What are the general advantages and disadvantages of material processing with laser radiation?
- Advantages:
a. The conversion of laser energy into thermal energy at the workpiece enables processing with a much higher quality.
b. In terms of energy field manufacturing, laser energy can be tailored to the material properties allowing a very flexible adjustment of the interaction that can lead to vaporization, melting, or just surface modification. - Disadvantages:
a. the relatively low electrical to laser optical conversion efficiency.
b. the high investment costs
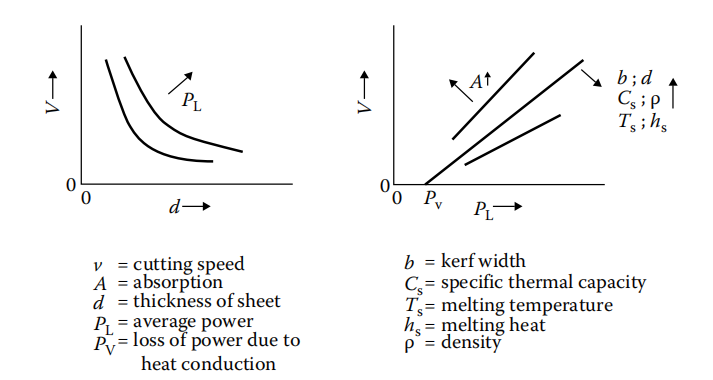
2、Which are the processing parameters during laser cutting? Show their interdependency.
- Processing parameters:
| 符号 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| d | thickness of sheet 板材厚度 |
| v | cutting speed 切割速率 |
| P | laser power 激光功率 |
| A | absorptivity 吸收率 |
- Interdependency:
a. With the same material and laser power(P), d and v are negatively correlated.
b. With the same material and thickness of sheet(d), P and v are positively correlated.
c. With the same environment, A and v is positively correlated. It means the speed of cutting will
be improved while the absorptivity is higher.
d. The value of A is affected by the material properties, such as melting temperaD ture, density, and the specific thermal capacity
3、Describe photochemical processing and photothermal processing. Discuss the relationship between laser pulse duration and the thermal relaxation time, in another word, laser excited electronic states and thermalization rate, in these two processes photochemical processing.
Conclusion: Laser pulse duration and the thermal relaxation time are are positively correlated, which means the thermal relaxation time will be reduced when laser pulse duration is reduced.
Inference:
We can use TT to represent the duration of laser pulse, while f=1Tf=1T. So when TT becomes lower, ff will
become higher. Due to the relationship of P=W∗fP=W∗f, where PP is a constant, so WW will be lower. It is easy to know the positive relationship between PP and dd (the penetration depth of laser), so dd will be lower, too.
The formula to calculate thermal relaxation time can be presented as below:
$$
t_r=\frac{d^2}{4k}
$$
where kk is also a constant that stands for the demision of heat dispersion. So if the duration of laser pulse is reduced, the thermal relaxation time will also be reduced.
4、Describe the advantages of laser surface processing over mechanical, chemical, and electric discharge texturing. Name three applications of laser surface processing.
- Advantages over mechanical texturing:
a. The laser power density is high, and the workpiece absorbs the laser and the temperature rises rapidly to melt or vaporize. Even materials with high melting point, high hardness and brittleness (such as ceramics, diamonds, etc.) can be processed by laser.
b. The laser head is not in contact with the workpiece, and there is no problem of wear of the processing tool;
c. The workpiece is free from stress and is not easily contaminated;
d. The laser beam is easy to control and easy to combine with precision machinery, precision measurement technology and electronic computer to achieve high automation of processing and high machining accuracy;
- Advantages over chemical texturing:
a. Alloying elements that are inserted in the near-surface area by laser power are completely molten in the process and change the chemical composition and therefore the properties of the material. Thus, low-cost substrate materials can be alloyed to create surface zones with a high quality.
b. the possibility of automation or the reducedgeneration of toxic by products.
- Advantages over electric discharge texturing:
a. Those non-conductive materials can be processed by laser, but cannot with electric discharge
b. If laser processing is used, the internal stress of the workpiece will not increase.
- Applications:
a. Laser cladding: The buildup of layers on a substrate material under the utilization of an additive material.
b. Repair welding: It is used for high-quality and expensive workpieces in the range of cladding.
c. Laser marking: It has great potential concerning resistance of the mark, high-contrast marking, and processing speed.
三、纳米制造部分

1、Summarize the application/impact of photolithography.
Photolithography is the most significant fabrication process that has revolutionized modern life. The manufacturing of modern gadgets, such as computers, digital TVs, radios, and cell phones, involves photolithography. At the same time, photolithography is acclicable to lots of materials, such as silicon, silica, copper, etc.
2、Why is there a need to develop non-photolithographic processes?
As the feature size gets smaller, the requirement for infrastructure gets prohibitively expensive and it is eventually impractical to continuously utilize photolithography in the fabrication of structures with dimensions less than tens of nanometers. The use of an optical field as the manufacturing field in photolithography has an ultimate limitation in the smallest feature sizes this field can handle and eventually it will be technically impossible to generate structures at nanometer scales.
3、Summarize the different fields used in several soft lithography processes.
Fabricate structures of mesoporous silica
Functional mesoporous silica-based waveguide shape
Hierarchically ordered mesoporous silica generated
The fabrication of nanocrystal laser
4、Summarize the applications of soft lithography and imprinting lithography.
Processing various materials into functional devices, including inorganic materials and fragile, bioactive materials
Generating micro and nano reactors for the synthesis of materials at nanometer sizes
5、What is the self-assembly process? How does it fit into intelligent energy field manufacturing?
Self-assembly is defined as the process of generating structures with nanometer dimensions by taking advantage of many different fields, such as the chemical field, biointeraction field, flow field, etc.
The future of nano-manufacturing development will focus highly on precision, low cost, adaptability to various applications, and being environmentally friendly. And at that time, we may rely more on self-assembly to make nano-structures, which leads to lower carbon footprint and being more friendly to environment.
| 英 | 中 |
|---|---|
| photolithography | 光刻技术 |
| fabrication | 制造 |
| gadgets | 小玩意儿 |
| silicon | 硅 |
| silica | 二氧化硅 |
| copper | 铜 |
| soft lithography | 软光刻 |
| imprinting lithography | 压印光刻 |
| self-assembly | 自组装 |
参考资料:
1、Intelligent Energy Field Manufacturing: Interdisciplinary Process Innovations
 支付宝打赏
支付宝打赏
 微信打赏
微信打赏
赞赏是不耍流氓的鼓励