TensorFlow 1.x 实战--训练BP神经网络
本文于
1238
天之前发表,文中内容可能已经过时。
BP(back propagation)神经网络是1986年由Rumelhart和McClelland为首的科学家提出的概念,是一种按照误差逆向传播算法训练的多层前馈神经网络,是目前应用中最基本的神经网络。
BP(back propagation)神经网络是1986年由Rumelhart和McClelland为首的科学家提出的概念,是一种按照误差逆向传播算法训练的多层前馈神经网络,是目前应用中最基本的神经网络。
运行环境:tensorflow1.14.0
新建程序文件 打开ide 我这里使用的是jupyter notebook,优点是容易调试,简单清爽。
在终端输入jupyter notebook即可在浏览器里面打开,windows是在cmd里面输入。
载入必要的库 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 import tensorflow as tfimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt%matplotlib inline from skimage.io import imreadfrom skimage.transform import resizeimport osimport random
载入封装好的函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 def weight_variable (shape ): initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, mean=0 , stddev=0.01 ) return tf.Variable(initial) def bias_variable (shape ): initial = tf.constant(0.1 , shape=shape) return tf.Variable(initial) def fulc (x,next_depth ): depth = x.get_shape()[-1 ].value w = weight_variable([depth, next_depth]) b = bias_variable([next_depth]) r = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(x, w), b)) return r
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 def load_images (path ): contents = os.listdir(path) classes = [each for each in contents if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(path,each))] print ('目录下有%s' % classes) labels = [] images = [] for each in classes: class_path = os.path.join(path,each) files = os.listdir(class_path) print ("Starting {} images" .format (each),'数量为' ,len (files)) for ii, file in enumerate (files, 1 ): img = imread(os.path.join(class_path, file)) img = img / 255.0 img = resize(img, (32 , 32 )) images.append(img.reshape((32 ,32 ,3 ))) labels.append(each) images = np.array(images) from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer lb = LabelBinarizer() lb.fit(labels) labels_vecs = lb.transform(labels) print ('总共读取了%d张图片' %images.shape[0 ]) return images,labels_vecs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 def next_batch (train_data, train_target, batch_size ): index = [ i for i in range (0 ,len (train_data))] np.random.shuffle(index); batch_data = np.zeros((batch_size,train_data.shape[1 ],train_data.shape[2 ],train_data.shape[3 ])); batch_target = np.zeros((batch_size,train_target.shape[1 ])); rand = random.randint(1 ,4 )*2 for i in range (0 ,batch_size): batch_data[i,:,:,:] = train_data[index[i],:,:,:] batch_target[i,:] = train_target[index[i],:] state = np.random.get_state() np.random.shuffle(batch_data) np.random.set_state(state) np.random.shuffle(batch_target) return batch_data, batch_target
封装神经网络结构 把上面的封装好的函数拿来用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 def create (x_images,keep_prob ): h,w,d=x_images.get_shape().value h_conv_flat = tf.reshape(x_images,[-1 ,h*w*d]) h_fc1 = fulc(h_conv_flat,1024 ) h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob) h_fc2 = fulc(h_fc1_drop,1024 ) h_fc2_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc2, keep_prob) h_fc3 = fulc(h_fc2_drop,1 ) out = tf.nn.sigmoid(h_fc3,name='out' ) print ('模型建立好了!' ) return out
tensorflow特色占位 在tensorflow1.x版本内,训练前需要先在内存中“占位”。
既然如此,我们把模型创建、损失函数的定义、准确率的定义也放到这一块。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 x_images = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None ,32 ,32 ,3 ],name='x_images' ) y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None ,1 ],name='y' ) keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,name='keep_prob' ) y_conv = create(x_images,keep_prob) pred = tf.round (y_conv,name='predict' ) cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_conv-y)),name='cross_entropy' ) train_step = tf.compat.v1.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4 ).minimize(cross_entropy) correct_prediction = tf.equal(pred,y) correct_prediction = tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(correct_prediction,name='accuracy' )
开始训练 训练目标:训练集{batch_x,batch_y}100%正确
训练集:从{train_x,train_y}中抽取20对
每10次迭代打印并记录一次loss&acc值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 saver = tf.compat.v1.train.Saver() with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer()) step = 1 acc=0 while acc!=1 : batch_x,batch_y = next_batch(train_x,train_y,20 ) _ = sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x_images: batch_x, y: batch_y, keep_prob: 0.75 }) if step % 10 == 0 : predt,acc,loss=sess.run([pred,accuracy,cross_entropy],feed_dict={x_images: batch_x, y: batch_y, keep_prob: 1. }) print ('step:%d,train loss:%f' % (step,loss)) print ('train accuracy:%f' % acc) with open ("trainloss.txt" ,"a+" ) as f: f.write('step:%d,train loss:%f\n' % (step,loss)) if step==10 : l = np.array(loss) a = np.array(acc) s = np.array(step) else : l = np.append(l,np.array(loss)) a = np.append(a,np.array(acc)) s = np.append(s,np.array(step)) step += 1 saver.save(sess,"./model/net.ckpt" )
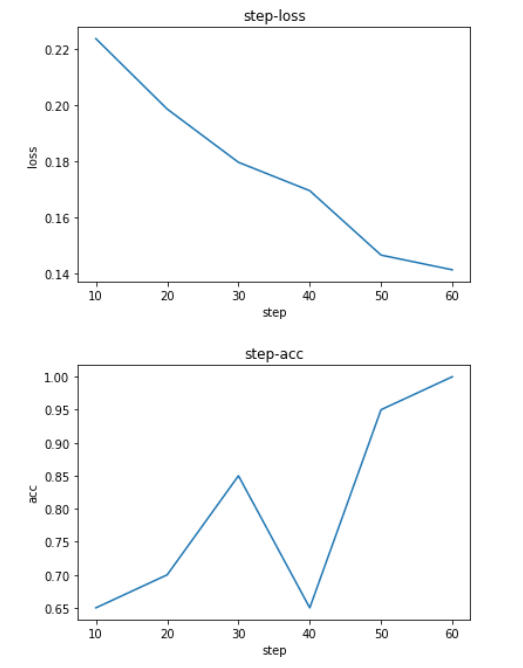
训练过程的可视化 使用以下代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 plt.plot(s,l)plt.title('step-loss' ) plt.xlabel('step' ) plt.ylabel('loss' ) plt.show() plt.plot(s,a) plt.title('step-acc' ) plt.xlabel('step' ) plt.ylabel('acc' ) plt.show()
效果如图:
最后: 本次实验中训练次数较少,且没有设置测试集或验证集,因此仅能作为参考,具体项目切不可如此。
 支付宝打赏
支付宝打赏
 微信打赏
微信打赏
 支付宝打赏
支付宝打赏
 微信打赏
微信打赏